The Cybersecurity Career Path: Skills, Roles, and Progression

Table of Contents
What Does a Cybersecurity Career Path Look Like?
Cybersecurity has become an increasingly important field in today’s digital world. With the rise of cyber threats and the need to protect sensitive information, cybersecurity professionals play a vital role in safeguarding data and systems. If you’re considering a career in cybersecurity, it’s important to understand what the career path looks like and the steps you can take to enter this exciting field.
Home
Introduction
In this article, we will explore the various aspects of a cybersecurity career path. We will discuss the skills and qualifications required, different job roles within the field, and the potential career progression options available. Additionally, we will provide insights into the current demand for cybersecurity professionals and the necessary steps to embark on this career journey.
Skills and Qualifications
A successful cybersecurity career requires a combination of technical skills, analytical thinking, and a strong understanding of information security principles. Some of the key skills and qualifications desired in this field include:
Technical Knowledge: Proficiency in areas such as network security, cryptography, penetration testing, and vulnerability assessment is essential for a cybersecurity professional.
Programming and Scripting: Familiarity with programming languages like Python, Java, and scripting languages like PowerShell can be valuable in performing security assessments and developing security tools.
Risk Assessment and Management: The ability to identify and assess potential risks, and develop strategies to mitigate them, is crucial in ensuring the security of an organization’s systems and data.
Communication and Collaboration: Strong communication skills are essential to effectively convey security risks and recommendations to stakeholders. Collaboration with different teams is also important for a holistic approach to cybersecurity.
Continuous Learning: Given the ever-evolving nature of cybersecurity threats, a commitment to continuous learning is vital. Staying updated with the latest trends and technologies is crucial for a successful cybersecurity career.## Job Roles in Cybersecurity
The field of cybersecurity offers a wide range of job roles, each with its own specific responsibilities and requirements. Here are a few prominent roles in the cybersecurity industry:
Security Analyst: Security analysts monitor and analyze systems for vulnerabilities and security breaches. They are responsible for investigating incidents, implementing security measures, and maintaining security tools.
Ethical Hacker: Ethical hackers, also known as penetration testers, identify vulnerabilities in systems and networks by simulating cyber attacks. They help organizations identify weak points and provide recommendations to enhance security.
Security Engineer: Security engineers design and implement secure systems and networks. They work on the technical aspects of cybersecurity, such as configuring firewalls, implementing intrusion detection systems, and conducting security audits.
Security Consultant: Security consultants provide expert advice and guidance to organizations regarding their security posture. They assess risks, develop security strategies, and assist in policy development and compliance.
Security Architect: Security architects design and build secure systems and networks from the ground up. They ensure that security controls and mechanisms are integrated into the architecture of an organization’s infrastructure.
Career Progression
The cybersecurity career path offers numerous opportunities for growth and advancement. As professionals gain experience and expertise, they can explore higher-level roles and responsibilities. Here are some potential career progression options:
Cybersecurity Specialist: After gaining experience in a specific domain of cybersecurity, professionals can become specialists in areas such as cloud security, network security, or incident response.
Security Manager: Security managers oversee a team of cybersecurity professionals and are responsible for developing and implementing security strategies, managing incidents, and ensuring compliance with regulations.
Chief Information Security Officer (CISO): CISOs are senior-level executives responsible for the overall cybersecurity strategy of an organization. They collaborate with other business units, manage budgets, and ensure alignment with industry regulations and best practices.
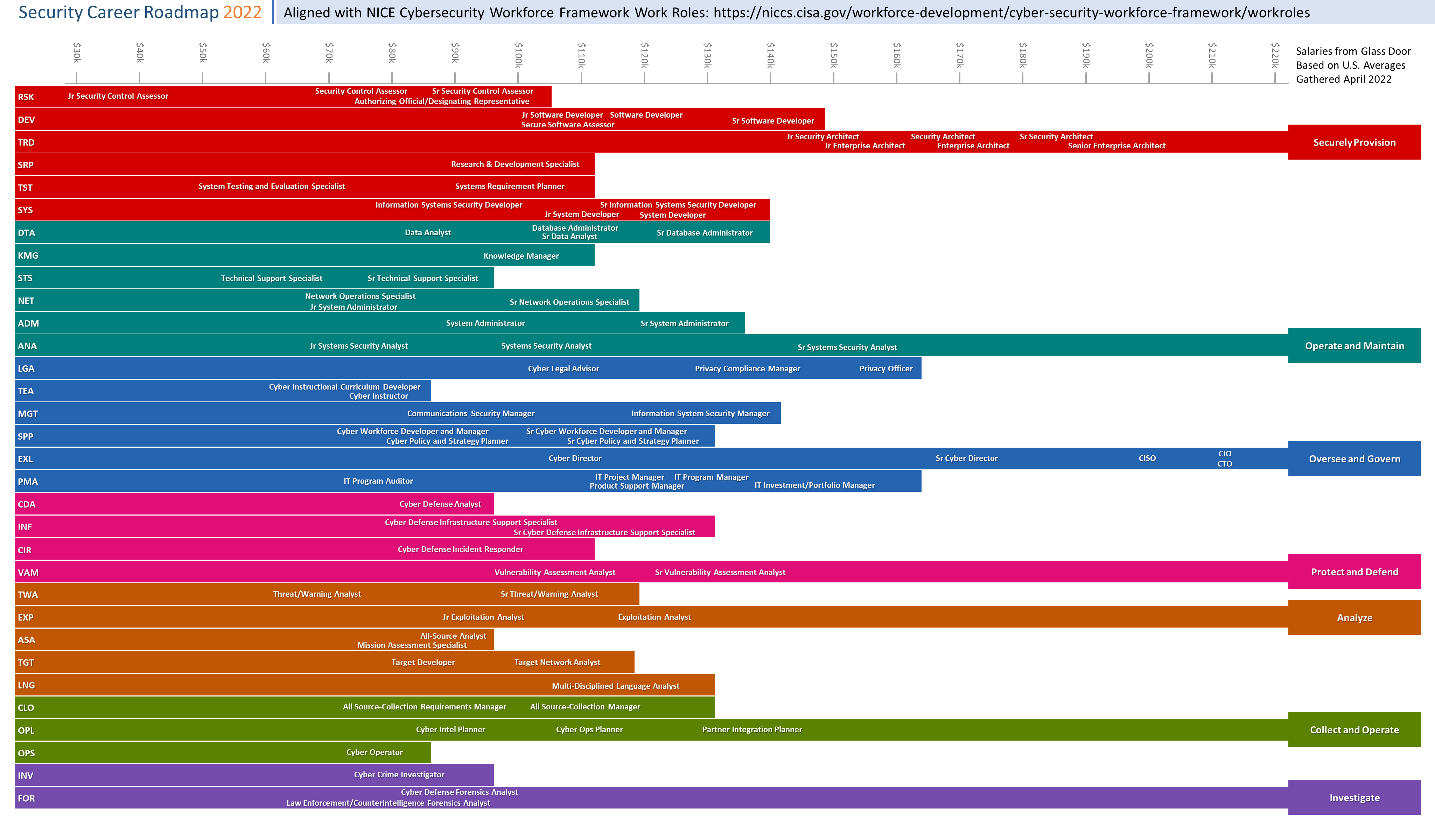
Cyber Security Career Roadmap Chart
This graph, made by Paul Jerimy , outlines Cyber Security and IT Career Paths as aligned with the NICE CyberSecurity Workforce Framework Work Roles .
Current Demand and Future Outlook for Cybersecurity Professionals
The demand for cybersecurity professionals is witnessing substantial growth as organizations increasingly prioritize safeguarding their digital assets. According to data from the Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS), the number of cybersecurity job openings has experienced a significant 35% increase in the past year. This trend is projected to continue, driven by the escalating sophistication of cyber threats.
Government regulations and industry standards also exert a significant influence on the demand for cybersecurity professionals. For example, specific government regulations outlined on the BLS website mandate organizations to implement robust cybersecurity measures and employ qualified professionals to ensure compliance.
Getting Started in Cybersecurity
To begin a career in cybersecurity, here are some steps you can take:
Education and Certification : Pursue a degree or certification in cybersecurity or a related field. Many institutions offer comprehensive programs to help individuals develop the necessary skills and knowledge.
Gain Practical Experience: Internships, part-time jobs, or volunteering in cybersecurity roles can provide valuable hands-on experience and exposure to real-world scenarios.
Networking and Professional Associations: Join cybersecurity-focused professional associations, attend industry events, and connect with professionals already working in the field. Building a strong network can lead to valuable opportunities and insights.
Continuous Learning: Stay updated with the latest trends, technologies, and industry developments through online courses, conferences, and industry publications. Continuously improving your skills will enhance your chances of success in the cybersecurity field.
Conclusion
A career in cybersecurity offers exciting opportunities to protect organizations from cyber threats and contribute to a safer digital world. By acquiring the necessary skills, gaining practical experience, and staying updated with the latest trends, you can embark on a successful cybersecurity career path. Remember, cybersecurity is a dynamic field, and continuous learning and adaptation are key to staying ahead.






