Certifications for Cybersecurity Careers: The Key to Success

Table of Contents
Home
Are Certifications Needed for a Cybersecurity Career?
Introduction
In the rapidly evolving field of cybersecurity, professionals often wonder whether certifications are necessary for a successful career. This article explores the significance of certifications, their benefits, and their relevance in the cybersecurity industry, with a particular focus on positions regulated by the Department of Defense (DoD).
The Importance of Certifications in Cybersecurity
Certifications serve as a validation of an individual’s knowledge and skills in specific areas of cybersecurity. They provide a standardized framework for assessing expertise and are widely recognized by employers and industry professionals. Obtaining certifications demonstrates a commitment to continuous learning and professional development, making it a valuable asset in the cybersecurity field.
Certifications and Skill Validation
One of the key advantages of certifications is the opportunity to validate your skills and knowledge in specific cybersecurity domains. Certification programs, such as CompTIA Security+, Certified Information Systems Security Professional (CISSP), and Certified Ethical Hacker (CEH), cover various aspects of cybersecurity and ensure that professionals have a comprehensive understanding of the subject matter.
Benefits of Certifications
Enhanced Job Opportunities: Certifications can significantly increase job prospects as many organizations require certified professionals to fill cybersecurity roles. This is especially true for positions regulated by the DoD, as stipulated by the DoD Directive 8570.1.
Career Advancement: Certifications provide a clear path for career progression. As you acquire higher-level certifications, such as Certified Information Security Manager (CISM) or Certified Information Systems Auditor (CISA), you can unlock new opportunities and command higher salaries.
Industry Recognition: Certifications are well-respected within the cybersecurity community. They establish credibility and demonstrate your commitment to staying updated with the latest industry standards and best practices.
Continual Learning: Maintaining certifications requires ongoing education and renewal, which encourages professionals to stay up-to-date with emerging threats, technologies, and trends in the cybersecurity landscape.
Government Regulations and Certifications
Government regulations, including those of the DoD, play a crucial role in shaping the cybersecurity landscape. Certain regulations, such as the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) guidelines or the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in the European Union, require organizations to maintain a certain level of cybersecurity measures. Certifications, such as ISO 27001 for information security management systems or Cybersecurity Maturity Model Certification (CMMC) for DoD contractors, can help organizations demonstrate compliance with these regulations.
Choosing the Right Certifications
When pursuing certifications, it is important to consider your career goals, interests, and the specific requirements of your desired job roles. Here are some popular certifications in the cybersecurity field:
- CompTIA Security+ : A foundational certification covering essential security concepts and best practices.
- Certified Information Systems Security Professional (CISSP) : A globally recognized certification for experienced cybersecurity professionals.
- Certified Ethical Hacker (CEH) : Focuses on ethical hacking techniques to identify and address vulnerabilities.
- Certified Information Security Manager (CISM): Designed for individuals managing, designing, and overseeing an enterprise’s information security program.
- Certified Information Systems Auditor (CISA): Focuses on auditing, control, and security of information systems.
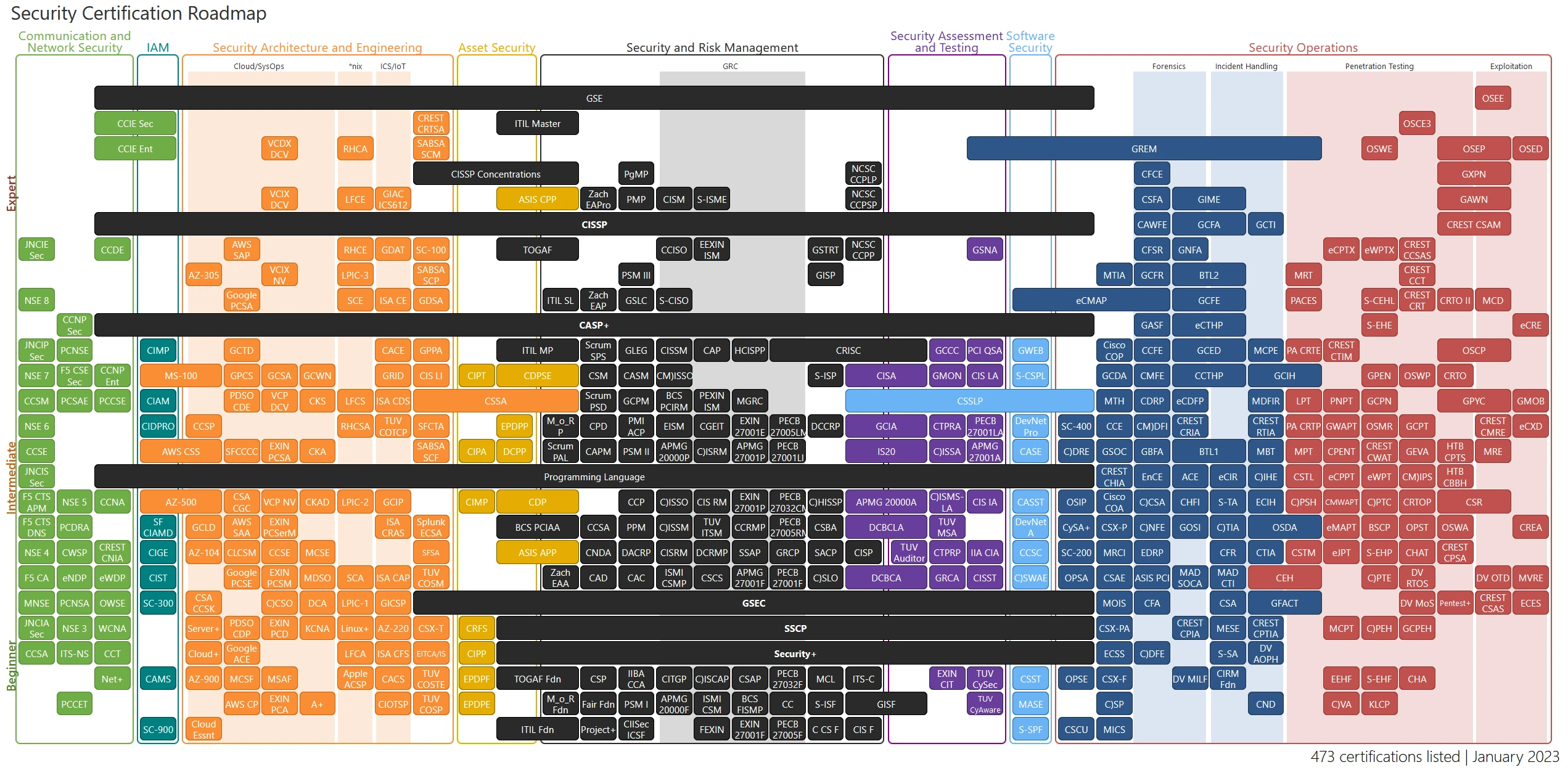
Certification Roadmap Chart
This graph, made by Paul Jerimy , outlines Cyber Security and IT Career certifications based on their covered Domains of Knowledge.
Conclusion
While certifications are not the sole determining factor for a successful cybersecurity career, they play a vital role in skill validation, job opportunities, career advancement, and industry recognition, particularly in positions regulated by the DoD as mandated by DoD Directive 8570.1. Earning certifications demonstrates your commitment to the profession and provides a competitive edge in the job market. As the cybersecurity field continues to evolve, staying current with certifications is essential for professional growth and maintaining relevance in this dynamic industry.
References:
- CompTIA Security+
- Certified Information Systems Security Professional (CISSP)
- Certified Ethical Hacker (CEH)
- Certified Information Security Manager (CISM)
- Certified Information Systems Auditor (CISA)
- National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST)
- General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR)
- ISO 27001
- Cybersecurity Maturity Model Certification (CMMC)