Speed Up Your CPU: Tackling Slow Performance Issues
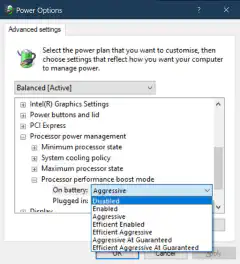
Table of Contents
Decoding Slow CPU Performance: Causes and Solutions
Slow CPU performance can be frustrating and can significantly impact the overall performance of your system. It can cause lag, slow down your applications, and even lead to system crashes. In this article, we will explore the causes of slow CPU performance and provide solutions to help you optimize your CPU performance.
Key Takeaways
- Insufficient cooling and overheating can lead to slow CPU performance.
- Outdated or incompatible hardware can cause CPU performance issues.
- Malware and background processes can consume CPU resources and slow down your system.
- High CPU usage by specific applications can impact overall performance.
- Inadequate power supply can result in slow CPU performance.
Understanding CPU Performance
What is CPU performance and why is it important?
CPU performance refers to the speed and efficiency at which a central processing unit (CPU) can execute instructions and perform tasks. It is a critical factor in determining the overall performance and responsiveness of a computer system.
- CPU performance directly affects the speed at which programs and applications run on a computer.
- A faster CPU can handle more complex tasks and calculations, resulting in quicker response times and improved multitasking capabilities.
- CPU performance is particularly important for resource-intensive activities such as gaming, video editing, and 3D rendering, where a slow CPU can lead to lag, stuttering, and reduced productivity.
To measure CPU performance, various benchmarks and metrics are used, including clock speed, number of cores, cache size, and instructions per cycle (IPC). These metrics provide an indication of the CPU’s processing power and efficiency.
Improving CPU performance can significantly enhance the overall user experience and productivity, making it an essential consideration for both casual users and professionals.
Factors that affect CPU performance
CPU performance can be influenced by several factors. Understanding these factors is crucial for optimizing and troubleshooting CPU performance.
1. Clock Speed: The clock speed of a CPU determines how many instructions it can execute per second. Higher clock speeds generally result in faster performance.
2. Number of Cores: CPUs with multiple cores can handle more tasks simultaneously, leading to improved performance in multitasking scenarios.
3. Cache Size: The CPU cache stores frequently accessed data, reducing the need to fetch data from slower memory. A larger cache size can enhance performance.
4. Architecture: The architecture of a CPU affects its efficiency and performance. Different architectures have varying capabilities and optimizations.
5. Thermal Design Power (TDP): TDP represents the maximum amount of heat a CPU generates under normal operation. CPUs with higher TDP may require better cooling solutions to maintain optimal performance.
To optimize CPU performance, it is important to consider these factors and ensure that the CPU is properly cooled and compatible with other hardware components.
The impact of slow CPU performance on system performance
Slow CPU performance can have a significant impact on the overall performance of a system. When the CPU is unable to process tasks efficiently, it can lead to sluggishness, delays, and decreased responsiveness. This can be particularly noticeable when running resource-intensive applications or multitasking.
In addition to affecting the speed of individual tasks, slow CPU performance can also impact the system’s ability to handle multiple processes simultaneously. This can result in a bottleneck effect, where the CPU becomes overwhelmed and struggles to keep up with the demands placed on it.
System freezes and crashes are also common symptoms of slow CPU performance. When the CPU is unable to handle the workload, it may become overloaded and cause the system to become unresponsive or even crash.
To illustrate the impact of slow CPU performance, consider the following table that compares the performance of a system with a slow CPU versus a system with a fast CPU:
| Task | Slow CPU Performance | Fast CPU Performance |
|---|---|---|
| Gaming | Choppy frame rates and lag | Smooth gameplay experience |
| Video editing | Slow rendering and exporting | Quick and efficient editing |
| Web browsing | Slow page loading times | Instant page responsiveness |
It is clear that slow CPU performance can significantly hinder the overall performance and user experience of a system. Therefore, it is crucial to address and resolve any issues that may be causing CPU slowdowns.
Common Causes of Slow CPU Performance
Insufficient cooling and overheating
Insufficient cooling and overheating can significantly impact CPU performance. When a CPU operates at high temperatures, it can lead to thermal throttling, where the CPU reduces its clock speed to prevent damage. This can result in slower processing speeds and decreased overall system performance.
To address insufficient cooling and overheating, consider the following:
- Ensure proper airflow in the computer case by cleaning dust and debris from fans and vents.
- Use high-quality thermal paste when installing or reseating the CPU cooler.
- Consider upgrading the CPU cooler to a more efficient model.
- Monitor CPU temperatures using software tools and take appropriate action if temperatures exceed recommended limits.
Note: Overclocking the CPU can also contribute to increased temperatures and should be done cautiously, considering the cooling capabilities of the system.
Taking steps to address insufficient cooling and overheating can help maintain optimal CPU performance and prevent potential damage to the CPU and other components.
Outdated or incompatible hardware
Outdated or incompatible hardware can significantly impact CPU performance. When the hardware components of a system are not compatible with each other or are outdated, it can lead to bottlenecks and inefficiencies in processing data. This can result in slower overall system performance and reduced productivity.
To address this issue:
- Ensure that all hardware components, such as the motherboard, processor, and RAM, are compatible with each other and meet the system requirements.
- Regularly check for firmware and driver updates for hardware components to ensure optimal performance.
- Consider upgrading outdated hardware components to improve compatibility and performance.
Note: Incompatible hardware can also cause system instability and crashes, so it’s important to address this issue to maintain a stable and efficient system.
Malware and background processes
Malware and background processes can significantly impact CPU performance. Malware refers to malicious software that can infiltrate a system and consume valuable CPU resources. It is essential to regularly scan for and remove any malware to ensure optimal CPU performance.
Background processes are tasks or programs that run in the background while the system is in use. These processes can consume CPU resources and slow down overall performance. Identifying and managing resource-intensive background processes is crucial for improving CPU performance.
To address the issue of malware and background processes, consider the following:
- Install and regularly update reliable antivirus software to detect and remove malware.
- Use a task manager or system monitoring tool to identify resource-intensive background processes.
- Disable or remove unnecessary startup programs to reduce the number of background processes running.
- Keep your operating system and applications up to date to minimize vulnerabilities that can be exploited by malware.
By taking these steps, you can mitigate the impact of malware and background processes on CPU performance and ensure a smoother computing experience.
High CPU usage by specific applications
High CPU usage by specific applications can significantly impact overall system performance. When certain applications consume a large amount of CPU resources, it can lead to slow performance, lag, and unresponsiveness. To address this issue, it is important to identify the applications that are causing high CPU usage and take appropriate actions. Here are some steps to help manage high CPU usage by specific applications:
- Monitor CPU usage: Use task manager or system monitoring tools to identify the applications that are consuming the most CPU resources.
- Close unnecessary applications: Close any unnecessary applications running in the background to free up CPU resources.
- Update or reinstall problematic applications: If a specific application is causing high CPU usage, try updating it to the latest version or reinstalling it to resolve any compatibility issues.
- Limit CPU usage: Some applications allow you to limit their CPU usage, which can help prevent excessive resource consumption.
- Consider alternative applications: If a particular application consistently causes high CPU usage, consider using alternative software that performs similar functions but with lower resource requirements.
Managing high CPU usage by specific applications is crucial for maintaining optimal system performance and ensuring a smooth user experience.
Inadequate power supply
An inadequate power supply can significantly impact CPU performance and overall system stability. When the power supply does not provide enough power to meet the demands of the CPU and other components, it can lead to various issues:
- Frequent system crashes due to insufficient power to run the CPU at its optimal performance level.
- Reduced processing speed as the CPU may not receive enough power to operate at its maximum frequency.
- Instability and random shutdowns when the power supply fails to deliver consistent power to the CPU and other components.
To ensure optimal CPU performance, it is important to have a power supply that can meet the power requirements of the system. Upgrading to a higher wattage power supply can help alleviate issues caused by an inadequate power supply. Additionally, checking the power supply’s efficiency rating and ensuring it is compatible with the system’s components can also contribute to better CPU performance.
Tip: When upgrading the power supply, consider factors such as the system’s power requirements, the efficiency rating, and the quality of the power supply to ensure reliable and stable power delivery.
Diagnosing Slow CPU Performance
Monitoring CPU temperature and usage
Monitoring the temperature and usage of the CPU is crucial for identifying potential performance issues. High CPU temperatures can lead to thermal throttling, where the CPU reduces its performance to prevent overheating. To monitor CPU temperature and usage, you can use hardware monitoring tools or software utilities. These tools provide real-time information on the temperature of the CPU and the percentage of CPU usage.
Here are some key points to consider when monitoring CPU temperature and usage:
- Ideal temperature range: The CPU should operate within a specific temperature range. Consult the manufacturer’s specifications to determine the ideal temperature range for your CPU.
- Temperature spikes: Monitor for sudden temperature spikes, as they may indicate a cooling issue or excessive CPU load.
- CPU usage patterns: Analyze the CPU usage patterns to identify any processes or applications that are consuming excessive CPU resources.
Tip: Regularly monitoring CPU temperature and usage can help prevent performance degradation and potential hardware damage.
Identifying resource-intensive processes
When diagnosing slow CPU performance, it is important to identify resource-intensive processes that may be causing the issue. Resource-intensive processes are those that consume a significant amount of CPU resources, leading to slower overall performance. Here are some steps to help identify these processes:
- Monitor CPU usage: Use task manager or a similar tool to monitor the CPU usage of different processes. Look for processes that consistently use a high percentage of CPU resources.
- Sort processes by CPU usage: Sort the processes by CPU usage to identify the ones that are using the most resources.
- Check for background processes: Some resource-intensive processes may run in the background without your knowledge. Check for any unnecessary or unwanted background processes that may be consuming CPU resources.
- Identify specific applications: If certain applications are causing high CPU usage, try to identify them and determine if they are necessary or if there are alternative options available.
By identifying and addressing resource-intensive processes, you can optimize CPU performance and improve overall system speed.
Checking for hardware compatibility issues
When experiencing slow CPU performance, it is important to check for any hardware compatibility issues. Incompatible hardware can significantly impact the overall performance of the CPU and the system as a whole. Here are some steps to help diagnose and address hardware compatibility issues:
- Check the motherboard compatibility: Ensure that the CPU is compatible with the motherboard. Refer to the motherboard’s documentation or manufacturer’s website for compatibility information.
- Verify RAM compatibility: Make sure that the RAM modules are compatible with the CPU and motherboard. Check the specifications of the CPU and motherboard to determine the supported RAM types and speeds.
- Confirm GPU compatibility: If using a dedicated graphics card, ensure that it is compatible with the CPU and motherboard. Check the GPU manufacturer’s website for compatibility information.
By addressing any hardware compatibility issues, you can optimize the CPU performance and improve the overall system efficiency.
Scanning for malware and unwanted programs
Scanning for malware and unwanted programs is an essential step in diagnosing slow CPU performance. Malware refers to malicious software that can significantly impact system performance. Unwanted programs are non-malicious software that may consume CPU resources and slow down the system. Here are some key points to consider:
- Use a reliable antivirus software to scan for malware and remove any detected threats.
- Regularly update the antivirus software to ensure it can detect the latest malware.
- Consider using additional anti-malware tools for a comprehensive scan.
- Remove any unwanted programs that are consuming CPU resources unnecessarily.
Tip: To prevent malware and unwanted programs from affecting CPU performance, avoid downloading software from untrusted sources and be cautious when clicking on suspicious links or email attachments.
It is important to regularly scan for malware and unwanted programs to maintain optimal CPU performance.
Testing power supply performance
Testing the performance of the power supply is crucial in diagnosing slow CPU performance. A faulty or inadequate power supply can lead to unstable voltage levels, which can negatively impact the CPU’s performance. To test the power supply, follow these steps:
- Use a multimeter to measure the voltage output of the power supply. Ensure that the voltages are within the specified range.
- Monitor the power supply’s performance under load by connecting a power-hungry device or running stress tests.
- Check for any unusual noises or excessive heat coming from the power supply, as these can indicate potential issues.
Note: If the power supply is found to be faulty, it is recommended to replace it with a reliable and sufficient power supply to ensure optimal CPU performance.
Optimizing CPU Performance
Upgrading hardware components
Upgrading hardware components can significantly improve CPU performance and overall system speed. By replacing outdated or underperforming components with newer, more powerful ones, you can experience faster processing speeds and smoother multitasking capabilities.
Here are some key considerations when upgrading hardware components:
- CPU: Upgrading to a faster and more advanced CPU can provide a substantial boost in performance. Look for CPUs with higher clock speeds, more cores, and improved architecture.
- RAM: Increasing the amount of RAM in your system allows for better multitasking and faster data access. Consider upgrading to higher capacity RAM modules or faster RAM speeds.
- Storage: Upgrading to a solid-state drive (SSD) can significantly improve system responsiveness and reduce loading times. SSDs offer faster data transfer speeds compared to traditional hard disk drives (HDDs).
Tip: Before upgrading hardware components, ensure compatibility with your motherboard and other existing components.
Investing in high-quality hardware upgrades can extend the lifespan of your system and provide noticeable performance improvements.
Optimizing software and removing bloatware
Optimizing software and removing bloatware can significantly improve CPU performance. By following these steps, you can ensure that your software is running efficiently and eliminate unnecessary processes that may be slowing down your CPU:
Uninstall unnecessary programs: Remove any software that you no longer use or need. These programs can consume valuable system resources and contribute to bloatware.
Disable startup programs: Prevent unnecessary programs from launching at startup, which can reduce the CPU load during booting.
Clean up temporary files: Regularly delete temporary files and clear cache to free up disk space and improve overall system performance.
Update software: Keep your software up to date to benefit from bug fixes, performance improvements, and security patches.
Optimize power settings: Adjust your power settings to prioritize performance over energy saving. This can help ensure that your CPU operates at its maximum potential.
Tip: Consider using a reputable software optimization tool to automate the process of removing bloatware and optimizing software settings.
By optimizing your software and removing unnecessary processes, you can enhance CPU performance and improve the overall speed and responsiveness of your system.
Managing startup programs and background processes
Managing startup programs and background processes is crucial for optimizing CPU performance. By controlling which programs and processes run at startup, you can reduce the overall CPU usage and improve system responsiveness. Here are some tips to effectively manage startup programs and background processes:
Disable unnecessary startup programs: Identify and disable programs that are set to run at startup but are not essential for your daily tasks. This can be done through the Task Manager or the System Configuration utility.
Prioritize critical processes: Identify the processes that are critical for your work or system functionality and ensure they have higher priority. This can be done through the Task Manager by adjusting the priority settings.
Use a startup manager tool: Consider using a startup manager tool that provides a user-friendly interface to manage startup programs and processes. These tools allow you to easily enable or disable programs, set priorities, and monitor resource usage.
Regularly review and update startup programs: Periodically review the list of startup programs and processes to ensure they are still necessary. Remove any programs that are no longer needed or causing excessive CPU usage.
Monitor resource usage: Keep an eye on the CPU and memory usage of startup programs and background processes. If you notice any abnormal or excessive resource usage, investigate and take appropriate action.
By effectively managing startup programs and background processes, you can optimize CPU performance and ensure smooth system operation.
Ensuring sufficient power supply
To ensure that your CPU has a sufficient power supply, there are a few key considerations:
- Check the power requirements of your CPU and ensure that your power supply meets or exceeds those requirements.
- Consider using a power supply calculator to determine the appropriate wattage for your system, taking into account all components.
- Invest in a high-quality power supply from a reputable manufacturer to ensure stability and reliability.
- Avoid using cheap or generic power supplies, as they may not provide consistent power delivery.
- Regularly monitor your power supply for any signs of failure or degradation, such as unusual noises or fluctuations in voltage.
Remember, a stable and sufficient power supply is crucial for optimal CPU performance and overall system stability.
Preventing Slow CPU Performance
Regular system maintenance and cleaning
Regular system maintenance and cleaning is essential for ensuring optimal CPU performance. By following a few simple steps, you can keep your system running smoothly:
Dust and debris removal: Over time, dust and debris can accumulate inside your computer, clogging the cooling system and hindering airflow. Regularly clean the vents, fans, and heat sinks to prevent overheating.
Software updates: Keep your operating system and software up to date. Updates often include bug fixes and performance improvements that can enhance CPU performance.
Disk cleanup: Perform regular disk cleanup to remove unnecessary files and free up storage space. This can help improve overall system performance, including CPU performance.
Defragmentation: If you’re using a traditional hard drive, regular defragmentation can optimize file storage and improve access times, leading to better CPU performance.
Uninstall unused programs: Remove any unnecessary or unused programs from your system. These programs can consume system resources and impact CPU performance.
By incorporating these practices into your regular system maintenance routine, you can help prevent slow CPU performance and ensure your system operates at its best.
Keeping hardware drivers up to date
Keeping hardware drivers up to date is crucial for maintaining optimal CPU performance. Outdated drivers can lead to compatibility issues, system instability, and reduced performance. To ensure that your hardware drivers are up to date:
- Visit the manufacturer’s website for each hardware component and check for driver updates.
- Download and install the latest drivers from the official sources.
- Consider enabling automatic driver updates if available.
Note: It’s important to download drivers only from trusted sources to avoid malware or compatibility issues.
Regularly updating hardware drivers not only improves CPU performance but also enhances system stability and security.
Using reliable antivirus software
Using reliable antivirus software is crucial for maintaining a secure and efficient system. Antivirus software helps protect your computer from malware, viruses, and other malicious threats. Here are some key points to consider when using antivirus software:
- Choose a reputable antivirus program that offers real-time protection and regular updates.
- Keep your antivirus software up to date to ensure it can detect and remove the latest threats.
- Perform regular scans of your system to identify and eliminate any potential threats.
- Configure your antivirus software to automatically scan new files and downloads.
By using reliable antivirus software, you can significantly reduce the risk of malware infections and improve the overall performance of your CPU and system.
Avoiding resource-intensive applications
To prevent slow CPU performance, it is important to avoid using applications that put a heavy strain on the CPU. These resource-intensive applications can significantly slow down your system and hinder overall performance. Here are some tips to help you avoid such applications:
- Choose lightweight alternatives: Opt for software that is designed to be efficient and uses fewer system resources.
- Close unnecessary background processes: Close any unnecessary programs running in the background to free up CPU resources.
- Limit multitasking: Avoid running multiple resource-intensive applications simultaneously to prevent CPU overload.
- Monitor CPU usage: Keep an eye on your CPU usage using task manager or other monitoring tools to identify applications that are consuming excessive resources.
By following these tips, you can ensure that your CPU is not burdened by resource-intensive applications, leading to improved system performance and responsiveness.
Investing in a quality power supply
Investing in a quality power supply is crucial for maintaining optimal CPU performance. A reliable power supply ensures a stable and consistent flow of electricity to the CPU, preventing power fluctuations that can lead to performance issues. Here are some key considerations when choosing a power supply:
- Wattage: Select a power supply with sufficient wattage to meet the requirements of your CPU and other components. Insufficient power can result in system instability and reduced performance.
- Efficiency: Look for power supplies with high efficiency ratings, such as 80 Plus certified models. These power supplies convert more of the AC power from the outlet into DC power for your components, reducing energy waste and heat generation.
- Modularity: Modular power supplies allow you to connect only the cables you need, reducing cable clutter and improving airflow within the system.
Investing in a quality power supply not only ensures optimal CPU performance but also contributes to the overall stability and longevity of your system.
Conclusion
In conclusion, CPU performance is a crucial aspect of system performance. A slow CPU can significantly impact the overall speed and efficiency of a computer. Understanding the factors that affect CPU performance, such as insufficient cooling, outdated hardware, malware, and high CPU usage, is essential for diagnosing and resolving performance issues. By monitoring CPU temperature and usage, identifying resource-intensive processes, checking for hardware compatibility issues, scanning for malware, and testing power supply performance, users can effectively diagnose the causes of slow CPU performance. To optimize CPU performance, cleaning and maintaining the cooling system, upgrading hardware components, optimizing software, managing startup programs and background processes, and ensuring a sufficient power supply are recommended. Additionally, preventing slow CPU performance can be achieved through regular system maintenance and cleaning, keeping hardware drivers up to date, using reliable antivirus software, avoiding resource-intensive applications, and investing in a quality power supply. By following these solutions, users can enhance CPU performance and improve the overall performance of their systems.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is CPU performance and why is it important?
CPU performance refers to the speed and efficiency at which a CPU can execute tasks. It is important because a faster and more efficient CPU can significantly improve the overall performance and responsiveness of a computer system.
What factors affect CPU performance?
Several factors can affect CPU performance, including the clock speed of the CPU, the number of cores and threads, the cache size, the architecture of the CPU, and the efficiency of the cooling system.
How does slow CPU performance impact system performance?
Slow CPU performance can lead to sluggish system performance, longer response times, lag in running applications, and overall reduced efficiency. It can also limit the ability to multitask and handle resource-intensive tasks.
What are the common causes of slow CPU performance?
Common causes of slow CPU performance include insufficient cooling and overheating, outdated or incompatible hardware, malware and background processes, high CPU usage by specific applications, and inadequate power supply.
How can I diagnose slow CPU performance?
You can diagnose slow CPU performance by monitoring CPU temperature and usage, identifying resource-intensive processes, checking for hardware compatibility issues, scanning for malware and unwanted programs, and testing power supply performance.
How can I optimize CPU performance?
To optimize CPU performance, you can clean and maintain the cooling system, upgrade hardware components, optimize software and remove bloatware, manage startup programs and background processes, and ensure sufficient power supply.