Ultimate XNET Guide - Optimize Your Installation

Table of Contents
XNET Carrier Offload Guide
Disclaimer: As of writing this, I’m considered to be an XNET Insider. Nothing you read here should be considered financial advice or to be speculative on the token price. This article is of my own writing and is not to be considered to be “official” and isn’t considered to be an endorsement by “XNET” by any means.
Introduction
In the rapidly evolving world of telecommunications, Wi-Fi offloading is becoming increasingly crucial as a method to alleviate network congestion and improve user experience. This guide delves into the XNET Carrier Offload system, explaining how it integrates with existing cellular networks to provide seamless connectivity. By employing Wi-Fi Passpoint technology, XNET helps carriers manage data traffic more effectively, thus enhancing service quality and reducing operational costs.
What is XNET Carrier Offload?
XNET Carrier Offload refers to the use of Wi-Fi networks to handle data traffic that would otherwise burden cellular networks. This technology is crucial for carriers in densely populated areas where mobile data traffic often exceeds network capacity. Using Wi-Fi Passpoint, also known as Hotspot 2.0, XNET ensures that mobile devices automatically connect to Wi-Fi networks, reducing load on cellular networks and improving user connectivity.
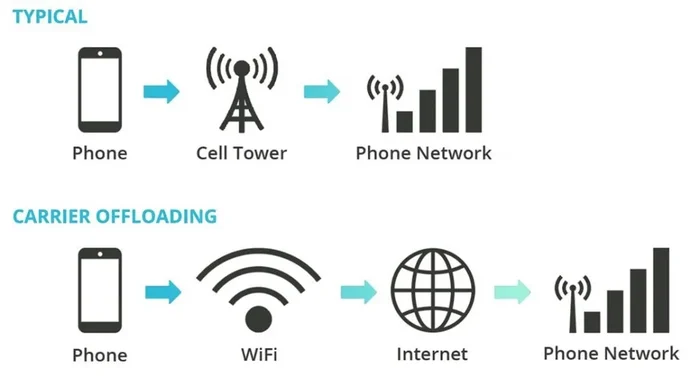
How Does XNET Carrier Offload Work?
Configuration and Partnership
XNET configures wireless access points with Passpoint technology and brokers offloading deals with cellular carriers. This partnership allows for the automatic transfer of mobile data traffic to Wi-Fi networks, seamlessly integrating with users’ mobile experiences.
Authentication and Connectivity
Cellular carriers provide a certificate to XNET, which is used to authenticate and announce to mobile devices that Wi-Fi offload is available. The seamless nature of this system means that users can connect to the internet without manual intervention, promoting a frictionless user experience.
Compensation Mechanism
Carriers compensate XNET based on the volume of data offloaded to the Wi-Fi network. Similarly, XNET incentivizes users by paying them in XNET tokens for each gigabit of data transferred via their network, promoting participation and network expansion.
Eligibility Regions for XNET Installation
XNET’s advanced Wi-Fi offloading services are available in a wide range of locations across North America, ensuring widespread access and connectivity enhancements. Below is a table detailing the specific regions in the United States and Canada where XNET installations are authorized. These areas have been selected based on their high traffic volumes and strategic importance for network optimization.
| Country | Eligible Locations |
|---|---|
| United States | All regions across the United States |
| Canada | Toronto, Ontario |
| Montreal, Quebec | |
| Vancouver, British Columbia | |
| Calgary, Alberta | |
| Edmonton, Alberta | |
| All International Airports | |
| Hotels & Resorts | |
| U.S. Border Crossings |
Disclaimer: The eligibility regions listed are verified as of the date of this article and are subject to change at any time.
This table serves as a quick reference for potential installers and users, highlighting the geographic reach and deployment capabilities of the XNET system. By maintaining installations in these key areas, XNET ensures optimal service delivery and network performance across major North American hubs.
Overview of XNET Wi-Fi Access Points: XT350, XR560, and XP6-Pro
Selecting the right Wi-Fi access point is crucial for optimizing network performance in various environments. XNET offers three distinct models—XT350, XR560, and XP6-Pro—each designed to meet different needs based on the venue size, user density, and specific usage scenarios. Below is a comparison table that outlines the primary features and capabilities of each model, helping you choose the most suitable option for your needs.
Comparison Table of XNET Wi-Fi Access Points
| Feature | XT350 Outdoor WiFi AP | XR560 Wi-Fi Access Point | XP6-Pro Wi-Fi AP |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ideal for | Outdoor and versatile environments | Large indoor venues | Small to medium indoor venues |
| Wi-Fi Standard | Wi-Fi 6 | Wi-Fi 6E | Wi-Fi 6 |
| MU-MIMO | 2x2 | 4x4 | 4x4 |
| Max Throughput | Up to 1.2 Gbps | Up to 4.7 Gbps | Up to 1.2 Gbps |
| Antenna Design | External, robust | Internal, high-performance | Internal, cost-effective |
| Price Point | High | High | Low (affordable) |
| Deployment | Parks, patios, outdoor venues | Conference centers, large offices | Cafes, small restaurants |
| Special Features | Weather-resistant, versatile | Tri-radio, advanced backhaul | Compact, easy to deploy |
| Power Over Ethernet (PoE) | Supported | Supported | Supported |
Key Differences and Suitability
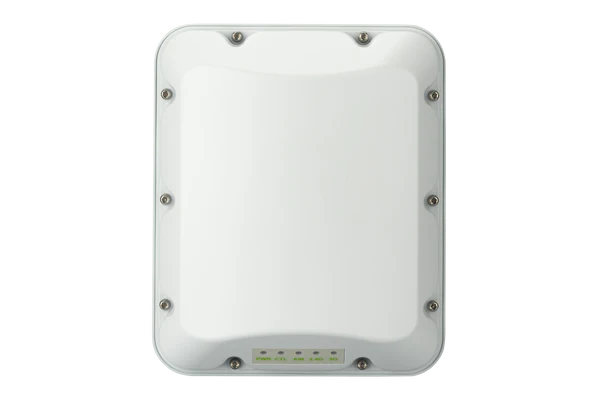

- XT350 Outdoor WiFi AP : With its Wi-Fi 6 capability and robust external antenna design, the XT350 is perfect for outdoor installations where durability and wide coverage are necessary. It’s ideal for areas like parks or outdoor cafés that require reliable internet access in a variety of weather conditions.
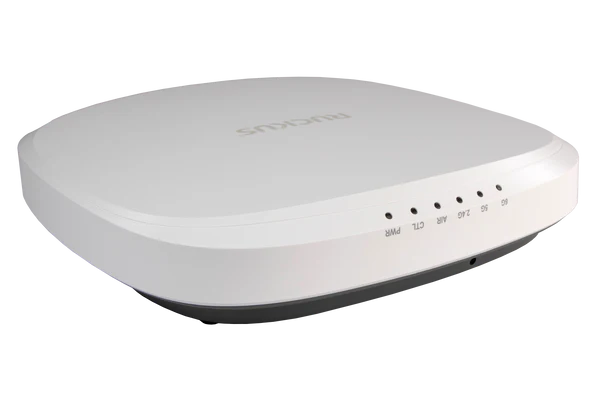

- XR560 Wi-Fi Access Point : This model is the powerhouse among the three, featuring Wi-Fi 6E technology for ultra-fast speeds and high capacity. The XR560’s advanced features, such as tri-radio and high-performance internal antennas, make it suitable for high-density environments like large offices or conference centers where many devices connect simultaneously.

- XP6-Pro Wi-Fi AP : As the most cost-effective option, the XP6-Pro offers good performance at a lower price point, making it accessible for smaller venues such as cafes and small restaurants. Its compact design and ease of deployment are significant advantages for places that need a straightforward, effective Wi-Fi solution without the complexities of more advanced models.
Each of these models offers distinct advantages, making them suitable for different types of environments and user needs. When selecting an XNET Wi-Fi access point, consider the specific requirements of your venue to ensure optimal performance and user satisfaction.
Ideal Installation Locations for XNET Offload
The effectiveness of XNET offloading significantly depends on its installation locations. Ideal places include high foot traffic areas such as airports, cafes, and public parks, where users often require quick internet access. Installing XNET in these areas ensures maximum usage and optimal offloading of cellular data traffic, providing a smooth user experience and reducing load on mobile networks.
List of Ideal Locations

- Airports: Constant influx of travelers needing quick access to data.
- Cafes and Coffee Shops: Popular with both local and visiting patrons who often stay for extended periods.
- Public Parks: Increasingly equipped with Wi-Fi for public use, especially in urban areas.
- Shopping Malls: Large numbers of visitors with high smartphone usage.
- Public Transit Stations: Subways, train stations, and bus terminals where people use downtime to browse the internet.
- University Campuses: Dense concentrations of tech-savvy students who frequently access online resources.
- Event Venues: Stadiums, concert halls, and conference centers with large crowds needing access to social media and online services.
- Libraries and Museums: Spaces where visitors stay for long periods and often need access to informational resources.
- Tourist Attractions: High traffic landmarks where tourists often require internet access for navigation and information.
- Large Hotels and Resorts: Guests and conference attendees utilize network access for both personal and business purposes.
Conversely, poor locations for XNET installations include isolated or low-traffic areas where the technology is underutilized, which leads to a waste of resources and potential revenue losses.
List of Poor Locations
- Single Family Residential Areas: Limited number of users, which doesn’t justify the infrastructure cost.
- Rural Locations: Sparse populations and low device density, leading to underutilization of network resources.
- Industrial Zones: Areas primarily for manufacturing or warehousing where there is minimal public access.
- Private Offices: Small businesses or corporate offices that do not receive significant external visitors.
- Areas with Low Pedestrian Traffic: Places where people primarily travel by car, such as remote rest stops or drive-through services.
- Non-Metro Residential Buildings: Apartment complexes in suburban or rural areas with insufficient user density.
- Farm and Agricultural Areas: Very low demand for public Wi-Fi given the nature of the location and work.
- Marinas and Boat Docks: Seasonal activity and often lack the necessary infrastructure for stable Wi-Fi.
- Construction Sites: Temporary setups and fluctuating crew sizes do not support permanent installations.
- Forests and Conservation Parks: Protected areas where modern infrastructure is often restricted to preserve natural conditions.
XNET Installation Examples and AP Placement Best Practices
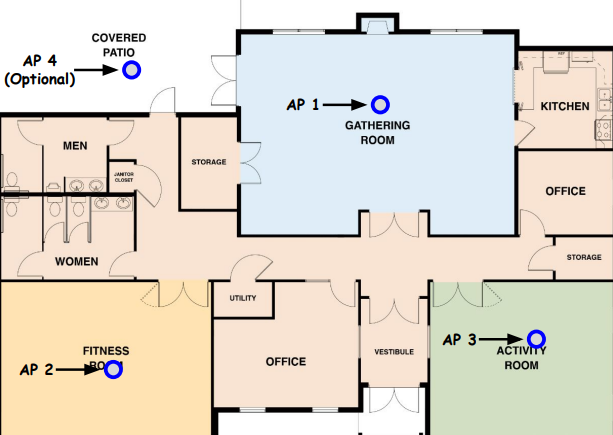
XNET Installation Example 1 - Clubhouse
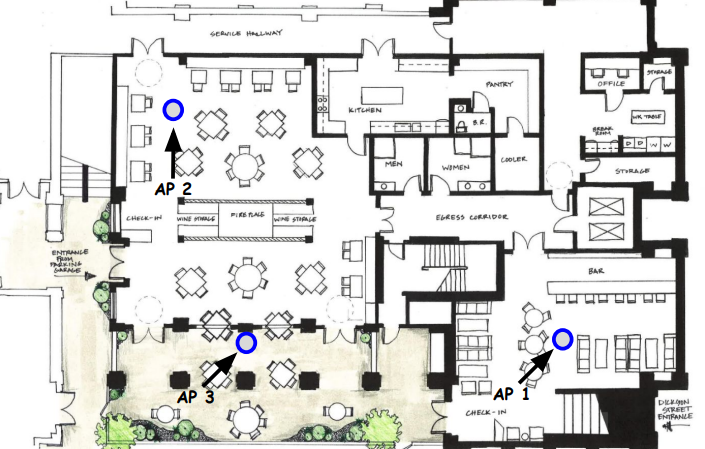
XNET Installation Example 2 - Restaurant
XNET Installation Example 3 - Meeting SPace
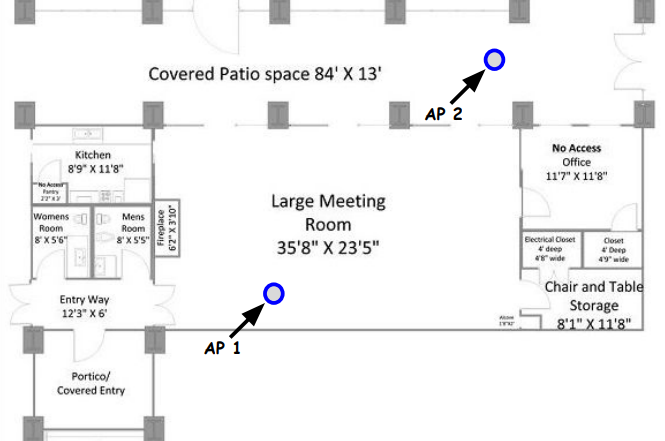
By strategically selecting the installation locations, XNET can maximize the utility and profitability of its Wi-Fi offloading service while enhancing connectivity for the largest number of users.
Installation Requirements and Best Practices
To ensure optimal performance of the XNET offload system, a minimum bandwidth of 100 Mbps download and 10 Mbps upload is necessary. Additionally, the installed bandwidth must meet or exceed the existing speeds in the area to prioritize XNET traffic effectively. Installation sites should be strategically chosen in metropolitan areas with a significant number of daily unique visitors and devices, maximizing the impact and efficiency of the offloading service.
Specifics on Installation Recommendations:
- Indoor installations being ceiling or high wall-mounted (above 8 feet) with minimal obstructions.
- Outdoor installations being pointed towards the dwelling area and not higher than 25 feet above the dwell area unless using a directional antenna.
Do’s and Don’ts
When setting up the XNET system, there are specific best practices and common pitfalls to avoid to ensure a reliable and efficient network. Below are detailed lists of do’s and don’ts that will guide the proper installation and maintenance of the XNET infrastructure.
Do’s
Here are essential practices to follow for optimal setup and operation:
| Do | Reasoning |
|---|---|
| Use compatible PoE injectors | Ensures that the power supply meets device specifications without risking damage. |
| Install in high-visibility areas | Maximizes usage and effectiveness of the network. |
| Regularly update firmware and software | Keeps the system secure and functioning efficiently. |
| Ensure proper physical security of APs | Prevents tampering and physical damage to the equipment. |
| Monitor network usage and adjust as needed | Optimizes performance and identifies potential issues early. |
Don’ts
Avoid these practices to prevent system failures and other complications:
| Don’t | Reasoning |
|---|---|
| Artificially consume bandwidth | Can lead to network abuse and potential banning by the carrier. |
| Modify or attempt to modify the hardware or software | Voids warranties and can disrupt service integrity. |
| Ignore environmental factors in outdoor installations | Exposure to harsh conditions can reduce the lifespan of hardware. |
| Neglect regular network performance evaluations | Failing to assess network health can lead to deteriorated user experiences. |
| Install without considering local regulatory compliance | Could result in legal issues and potential network shutdowns. |
By adhering to these guidelines, installers and maintainers of the XNET system can ensure that the network remains robust, secure, and capable of handling the intended traffic load. Proper adherence to these practices not only enhances the performance but also extends the lifespan and effectiveness of the XNET offload infrastructure.
Real-Time Network Monitoring with XNET Dashboard Limitations
The XNET Dashboard provides useful insights and management tools for users but currently does not support the display of Wi-Fi devices connected to the network. This means that users seeking detailed, real-time metrics of their network activity will need an alternative solution.
Alternative for Real-Time Monitoring
For users requiring real-time network monitoring, we recommend the GL.iNet GL-SFT1200 (Opal) Secure Travel WiFi Router . This device is not only affordable but also offers comprehensive features for robust network management.
The router can be integrated with GoodCloud.xyz , a cloud management service, allowing for real-time and remote monitoring of network activities across your offload devices. For more information and to purchase, visit Amazon .
Security and Compliance
Ensuring the security and integrity of user data and network operations is paramount for XNET systems, especially when offloading cellular data traffic to Wi-Fi networks. XNET employs robust security measures and compliance practices to maintain a high standard of protection.
Network and Data Security Protocols
XNET Carrier Offload incorporates several sophisticated security protocols designed to ensure the security and privacy of carrier traffic, particularly focusing on the encryption of calls, SMS, and MMS.
Encrypted Carrier Traffic
All mobile carrier traffic that passes through XNET, including voice calls, SMS, and MMS, is securely tunneled through a VPN provided by the cellular carrier. This VPN ensures that all such communications are encrypted at all times, safeguarding the privacy and security of sensitive information transmitted over the network. This arrangement is crucial for maintaining the confidentiality of user communications, particularly in environments where network security cannot be guaranteed.
HTTPS for General Traffic
Aside from carrier-specific communications, the rest of the traffic from mobile devices relies on HTTPS for encryption. HTTPS, or Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure, is an internet communication protocol that protects the integrity and confidentiality of data between the user’s device and the site. Users can rest assured that their browsing activities and data transfers are secured through this protocol, even when connected to public Wi-Fi networks like those provided by XNET.
Network Isolation and Visibility
The configuration of XNET access points (APs) is specifically designed to enhance security by isolating them from local network devices. This means that while connected to an XNET AP, your device will not be able to see other local devices on the network. Conversely, other devices cannot see your device, although they are technically on the same network. This isolation helps prevent unauthorized access and data breaches within the network.
Advanced User Options for Increased Security
Although XNET APs provide a basic level of security, users with higher security needs can take additional measures if their network hardware supports it:
- VLANs: Implementing Virtual Local Area Networks (VLANs) can further segment the network, creating isolated networks within the broader network that can help control which devices and traffic can communicate with each other.
- Firewall Rules: Setting up advanced firewall rules can provide an additional layer of security, controlling incoming and outgoing network traffic based on predetermined security rules.
Public Internet Access
Importantly, XNET APs are configured to only require access to the public internet and do not need to interact with local network resources. This design minimizes the risk of internal network threats and simplifies the network setup, focusing solely on providing secure, reliable internet access to users.
By implementing these protocols, XNET ensures that all carrier communications remain secure and private, while also providing flexible options for users and organizations that require enhanced network security measures.
Use of Public IP and VLAN Settings:
XNET systems are designed to operate within a public IP framework, which enhances accessibility and integration with existing network infrastructures. However, this also necessitates rigorous security measures. The use of private space and DHCP configurations on VLAN ensures that each device connected through XNET has a unique network identity, thereby minimizing potential IP conflicts and enhancing network security.
Authentication and Logging:
Authentication is a critical aspect of security for XNET. Each device that connects to the network must be authenticated to ensure that it is authorized to use the XNET service. This is typically managed through digital certificates provided by the cellular carriers, as part of the Wi-Fi Passpoint standard. Logging of user activities is also conducted meticulously to ensure a trail of data usage and system access, which is vital for auditing and addressing any potential security incidents.
Content Filtering and DNS Providers
DNS Filtering: To further secure the network against malicious activities, content filtering DNS providers are recommended. These providers help filter out harmful or suspicious websites by blocking the DNS lookup that would normally enable users to access such sites. This is particularly important in public Wi-Fi networks like those managed by XNET, where users might inadvertently access compromised sites or download malware.
Benefits of DNS Filtering:
- Protection Against Phishing: Reduces the risk of accessing phishing sites that can steal user information.
- Block Malware: Helps prevent devices from connecting to sites known to distribute malware.
- Control Content Access: Enables network administrators to block access to inappropriate or undesirable websites, maintaining compliance with corporate policies or legal standards.
Compliance with Telecommunications Standards
Regulatory Adherence: XNET operations align with all relevant government regulations concerning data security and telecommunications. This includes compliance with standards set by organizations such as the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) and international telecommunications bodies. Compliance ensures that XNET not only protects user data but also operates within legal frameworks, avoiding potential legal issues and fines.
Regular Audits and Updates: To maintain compliance and security, XNET systems undergo regular audits to check for vulnerabilities and to ensure that all components of the network are operating correctly. Updates to software and firmware are conducted as needed to address security vulnerabilities, enhance functionality, and stay aligned with current security practices and standards.
By integrating these security measures, XNET ensures a secure and compliant environment for users and carriers alike, promoting safe and efficient data offloading and connectivity. These practices underscore XNET’s commitment to maintaining the highest standards of security and compliance in its operations.
FAQs on XNET Carrier Offload
Here’s a quick Q&A to provide clarity on common inquiries regarding the XNET Carrier Offload system:
Who uses XNET Mobile?
- Customers from AT&T, AT&T FirstNet, Consumer Cellular, Cricket Wireless, Google-Fi, and other major carriers in the future.
What are the benefits of Wi-Fi offloading?
- Reduced network congestion: Offloads traffic to Wi-Fi to alleviate cellular network load.
- Improved user experience: Provides smoother, faster internet access.
- Cost savings for carriers: Decreases the need for expensive network infrastructure upgrades.
How are users compensated?
- Users receive XNET tokens for the data they offload, which can be used for various services or converted to other forms of value.
Conclusion
XNET Carrier Offload is a pivotal technology in modern telecommunications, facilitating enhanced data management and user connectivity. By understanding and implementing this system effectively, carriers can ensure sustained growth and improved service delivery in the face of rising data demands.
References
- Wi-Fi Alliance: Wi-Fi Passpoint
- Federal Communications Commission on Telecommunications Standards
- Network Bits Crypto Slide Deck
- What is Carrier Offloading?
- XNET Company Documentation
- XNET Shop
Disclosure and Affiliate Statement:
Affiliate Disclosure: We may earn a commission from links on this page. These commissions support our website and the content we provide. Rest assured, we only recommend products/services we believe in. Thank you for your trust! Click Here to Learn More


